- 为什么css放头部,script放底部
@import的使用方式- flex-shrink
- a.x = a = {n:2} 问题
- let 和 var 编程题
为什么css放头部,script放底部
mdn官方解释
**注:**我们将
script放在HTML文件的底部附近的原因是浏览器会按照代码在文件中的顺序加载 HTML。如果先加载的 JavaScript 期望修改其下方的 HTML,那么它可能由于 HTML 尚未被加载而失效。因此,将 JavaScript 代码放在 HTML页面的底部附近通常是最好的策略。
CSS 不会阻塞 DOM 的解析,但会阻塞 DOM 渲染。
JS 阻塞 DOM 解析,但浏览器会"偷看"DOM,预先下载相关资源。
浏览器遇到 <script> 且没有defer或async属性的 标签时,会触发页面渲染,因而如果前面CSS资源尚未加载完毕时,浏览器会等待它加载完毕在执行脚本。
@import 的使用方式
@import会导致重新重新创建一个http链接,性能有所下降,所以不建议使用。
-
link属于html标签,而@import是css提供的。
-
页面被加载时,link会同时被加载,而@import引用的css会等到页面加载结束后加载。
-
link是html标签,因此没有兼容性,而@import只有IE5以上才能识别。
-
link方式样式的权重高于@import的。
注意
- import规则一定要先于除了@charset的其他任何CSS规则,相当于
@import必须处于当前样式表中最开始的位置
/css/style.css
@import "./style2.css";
.box {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: sandybrown;
}/css/style2.css
.box1 {
background-color: red;
}
.box2 {
background-color: skyblue;
}
.box3 {
background-color: gold;
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/style.css">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box box1"></div>
<div class="box box2"></div>
<div class="box box3"></div>
</body>
</html>自动忽略后两个请求(vscode 插件的额外请求),可以看出 加载 style.css 后,又会加载 style2.css
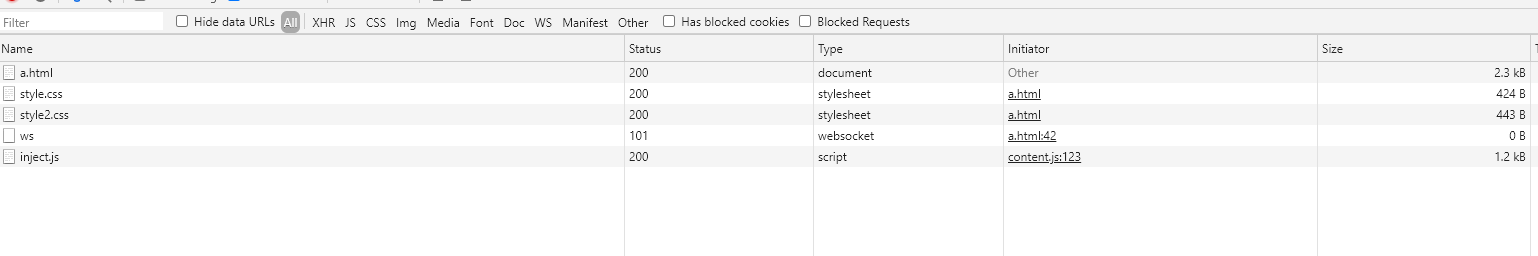
对于如下代码,.box1、.box2、.box3、.box4从顶到底的层叠顺序是?
<div class="box box1">
box1 relative
<div class="box box2">
box2 > box2 absolute
</div>
</div>
<div class="box box3">
box3 absolute
<div class="box box4">
.box3 > box4 relative
</div>
</div>
<style>
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.box {
height: 200px;
padding: 20px;
margin: 20px;
border: 1px solid;
}
.box1 {
position: relative;
z-index: 4;
background: red;
}
.box2 {
position: absolute;
left: 10px;
z-index: 3;
background: blue;
}
.box3 {
position: absolute;
z-index: 2;
top: 130px;
left: 60px;
background: yellow;
}
.box4 {
position: relative;
z-index: 5;
background: pink;
}
</style>正确顺序:2、1、4、3
解析
-
首先看
box1与box2,两元素为父子元素,子元素层级默认高于父元素(尽管本例中设置z-index值 父元素大于子元素)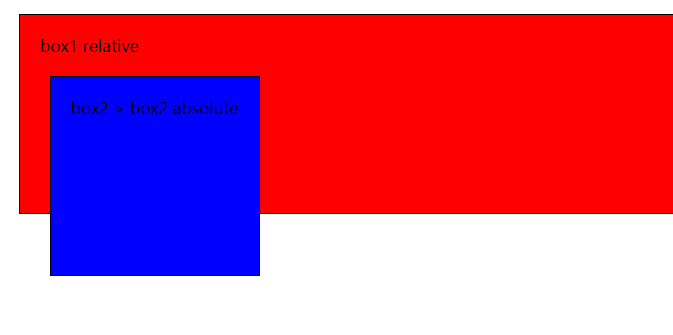
-
其次,
box3和box4也一样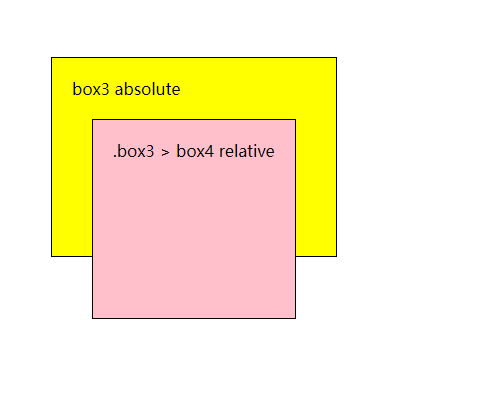 、
、 -
接着比较
box1和box3两兄弟元素box1的z-index值大于box3所以在上层,而子元素也随着父级的层级进行排列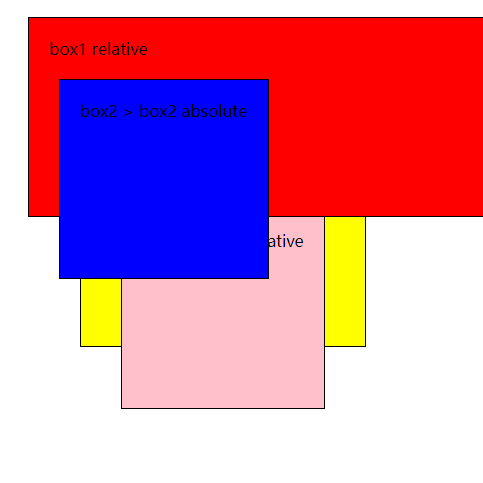
-
本文讲的不够详细,仅供参考
flex-shrink
前辈探索:
https://segmentfault.com/q/1010000023032378#comment-area
非官方文档解释:
父元素设置 display: flex; ,若子元素溢出,则根据规则计算平均分配每个元素缩放比例。
计算方式是先求所有item flex-shrink * flex-basis(width) 之和,
a.x = a = {n:2} 问题
let a = { n: 1 }
let b = a
a.x = a = { n: 2 }
console.log(a.x)
console.log(b.x)前辈探索:
https://yanhaijing.com/javascript/2012/04/05/javascript-continuous-assignment-operator/
let 和 var 编程题
let a = 5
var b = 8
let obj = {
a: 6,
b: 9,
foo() {
let a = 7
return this.a
},
bar: () => {
return this.b
},
}
console.log(obj.foo()) // 6
console.log(obj.foo.call()) // undefined
console.log(obj.bar()) // 8
console.log(obj.foo.call({ a: 2 })) // 2
// 不可以删除
delete window.b
console.log(window.b)注意
-
var 有全局作用域提升特性,全局定义的
var变量会自动绑定到 window 上,但 let 定义的变量则不可以 -
全局对象
window只读,不可修改,还有,不可以用delete语法删除全局对象window其中的属性 -
全局定义函数,也会绑定到window上