翻译自作者
bytefish文章 You Must Understand These 14 JavaScript Functions
1. 确定任意对象的指定类型
总所周知,在 JavaScript 中有6个原始数据类型(Boolean, Number, String, Null, Undefined, Symbol)当然还有对象数据类型。但是你知道对象数据类型能被分割成很多子类型吗?一个对象可能为一个 array,function, map 等等类型。如果我们想要获得一个对象的具体类型,应该怎么做?
代码
function toRawType (value) {
let _toString = Object.prototype.toString;
let str = _toString.call(value)
return str.slice(8, -1)
}解释
ECMAScript 有如下定义:

对于不同对象,当调用 Object.prototype.toString() 将会返回不同的结果。

此外, Object.prototype.toString() 返回值的格式为 [object tag] 。如果我们只想要中间的 tag ,我们可以通过正则匹配或 String.prototype.slice()来获取。
范例
toRawType(null)
// "Null"
toRawType(/sdfsd/)
//"RegExp
2. 缓存函数计算结果
如果有这么一个函数:
function computed(str) {
// 假设函数运行非常耗时
console.log('2000s have passed')
return 'a result'
}我们想要去缓存函数运行后的结果。当被调用后,如果参数一样,这个函数将不再被计算,结果在缓存中将会立马被返回。
代码
function cached(fn) {
// 创建一个对象去存储每个函数执行后返回的结果
const cache = Object.create(null);
// 返回一个 wrapped 函数
return function(str) {
if( !cache[str] ) {
let result = fn(str);
// 存储函数执行后的结果在缓存中
cache[str] = result;
}
}
}范例

3. 实现 Array.prototype.map
这是一个非常有用的 JavaScript 内置方法,但是你也应能够自己实现这个函数。
代码
const selfMap = function (fn, context) {
let arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(this)
let mappedArr = Array()
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (!arr.hasOwnProperty(i)) continue;
mappedArr[i] = fn.call(context, arr[i], i, this)
}
return mappedArr
}
Array.prototype.selfMap = selfMap;范例

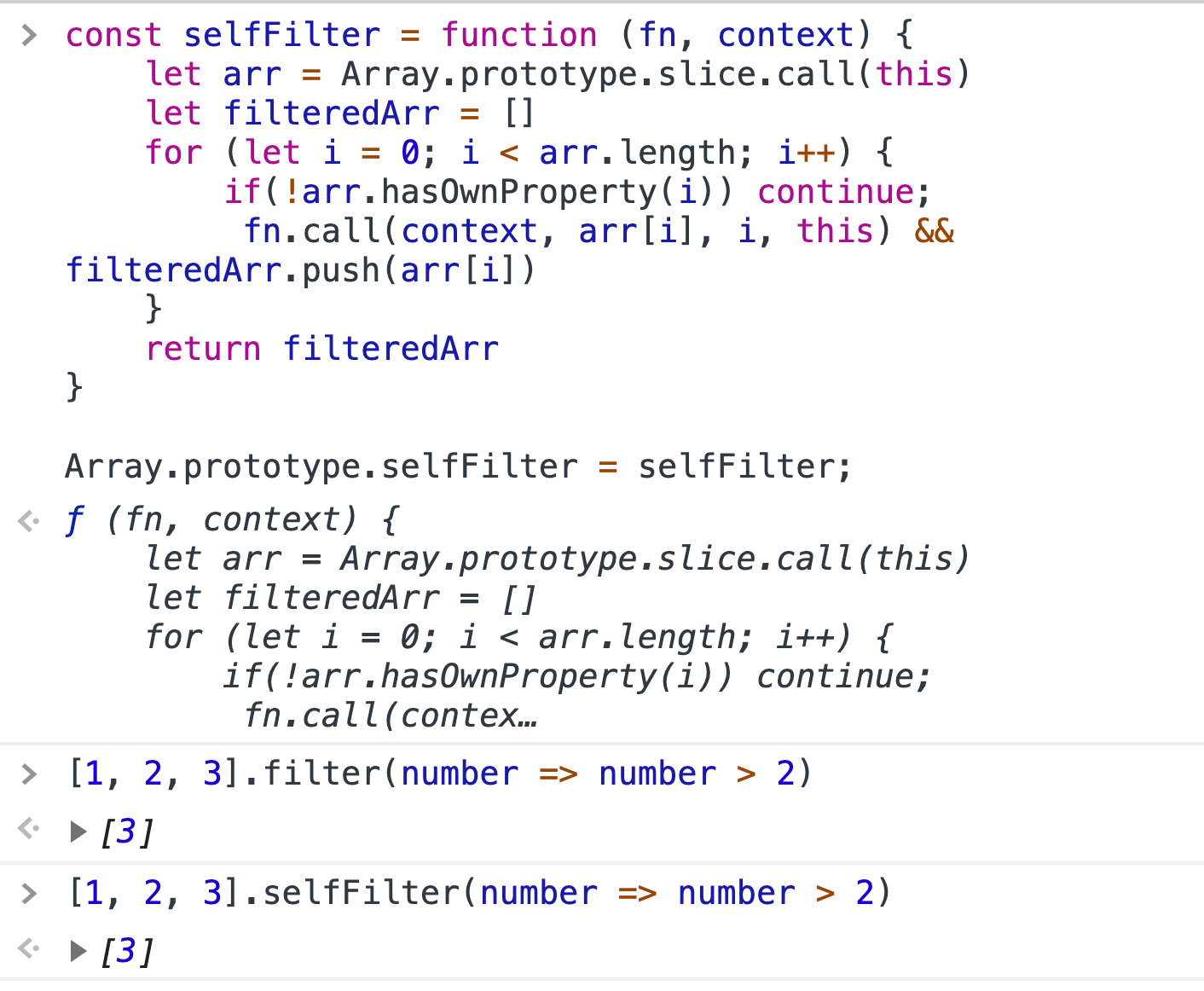
4. 实现 Array.prototype.filter
这是一个非常有用的 JavaScript 内置方法,但是你也应能够自己实现这个函数。
代码
const selfFilter = function (fn, context) {
let arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(this)
let filteredArr = []
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(!arr.hasOwnProperty(i)) continue;
fn.call(context, arr[i], i, this) && filteredArr.push(arr[i])
}
return filteredArr
}
Array.prototype.selfFilter = selfFilter;范例
5. 实现 Array.prototype.some
代码
const selfSome = function (fn, context) {
let arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(this)
if(!arr.length) return false
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(!arr.hasOwnProperty(i)) continue;
let res = fn.call(context,arr[i],i,this)
if(res)return true
}
return false
}
Array.prototype.selfSome = selfSome;范例

6. 实现 Array.prototype.reduce
代码
const selfReduce = function (fn, initialValue) {
let arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(this)
let res
let startIndex
if (initialValue === undefined) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (!arr.hasOwnProperty(i)) continue
startIndex = i
res = arr[i]
break
}
} else {
res = initialValue
}
for (let i = ++startIndex || 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (!arr.hasOwnProperty(i)) continue
res = fn.call(null, res, arr[i], i, this)
}
return res
}
Array.prototype.selfReduce = selfReduce;范例

7. 实现 Array.prototype.flat
代码
const selfFlat = function (depth = 1) {
let arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(this)
if (depth === 0) return arr
return arr.reduce((pre, cur) => {
if (Array.isArray(cur)) {
return [...pre, ...selfFlat.call(cur, depth - 1)]
} else {
return [...pre, cur]
}
}, [])
}
Array.prototype.selfFlat = selfFlat;范例

8. 科里化
科里化是一个将多个参数的函数求值转换为单个参数的函数序列的技术。
换言之,当一个函数不是一次获取所有参数,而是获取第一个参数并返回一个新函数,该函数获取第二个参数并返回一个新函数,该函数获取第三个参数,依此类推,直到所有参数都已完成。
为什么有用?
- 科里化帮你避免一遍又一遍的传递同一个变量
- 可以创建一个高阶函数,对于时间处理非常有用。
- 一小块儿(代码)能够配置和重复使用。
让我们一起来看下一个简单的 add 函数。它接受三个参数运算,并且将三个参数的和作为结果返回。
function add(a,b,c) {
return a+b+c;
}你调用它时可以传入很少的参数(结果很怪),或者传入很多参数(多余的将会被忽略)。
add(1,2,3) --> 6
add(1,2) --> NaN
add(1,2,3,4) --> 6 //Extra parameters will be ignored.
如何将一个已存在的函数转化为颗粒化版本?
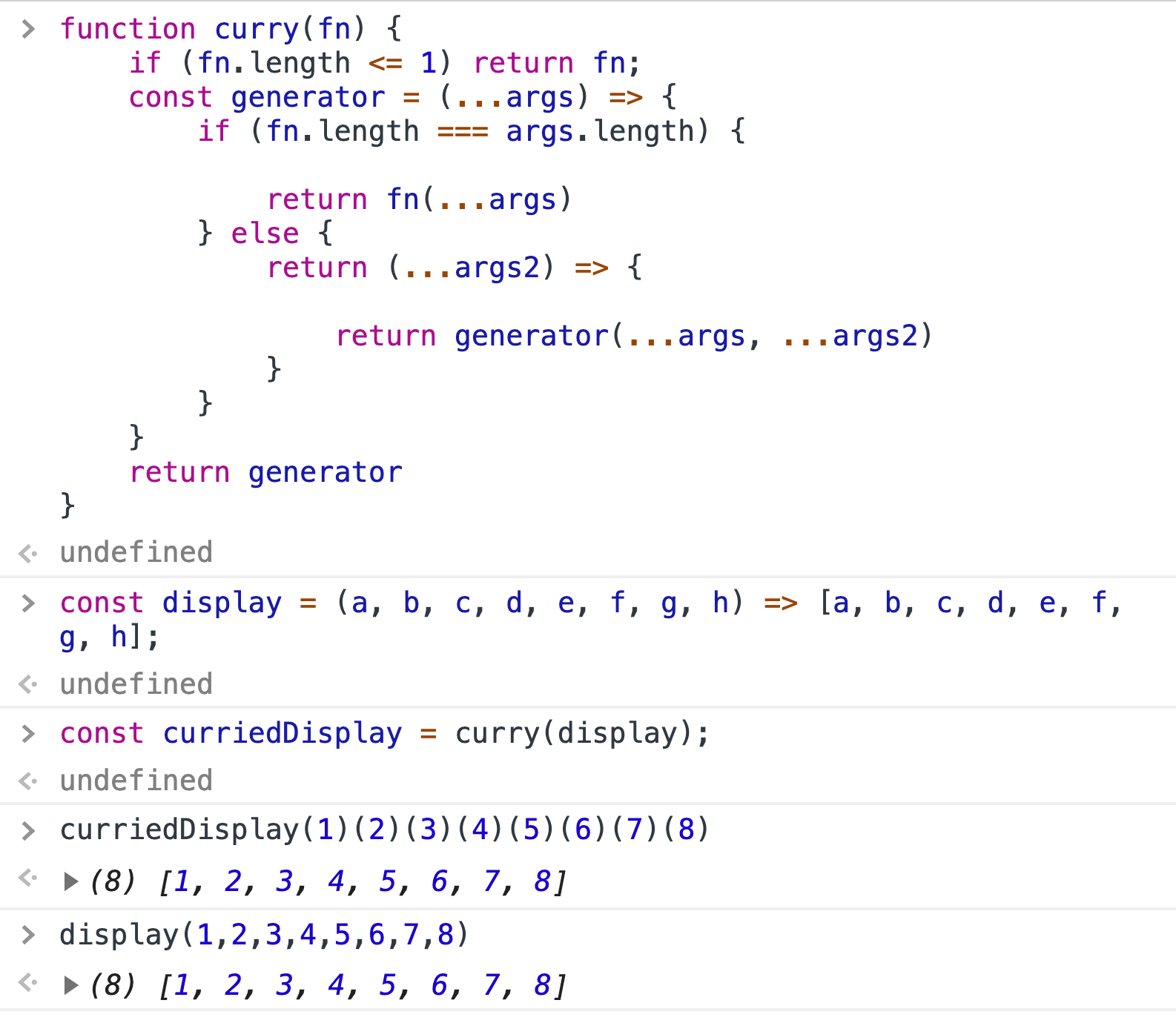
代码
function curry(fn) {
if (fn.length <= 1) return fn;
const generator = (...args) => {
if (fn.length === args.length) {
return fn(...args)
} else {
return (...args2) => {
return generator(...args, ...args2)
}
}
}
return generator
}范例
9. 防抖(debouncing)
防抖只不过是减少不必要的耗时计算,从而提高浏览器性能。在某些情况下,某些功能需要更多时间来执行某个操作。例如,以电子商务网站上的搜索栏为例。 假设用户想要获得“Tutorix study kit”。他在搜索栏中键入产品的每个字符。输入每个字符后,会从浏览器到服务器进行 Api 调用,以获取所需的产品。由于他想要“Tutorix study kit”,因此用户必须从浏览器到服务器进行 17 次 Api 调用。想象一个场景,当数百万人进行相同的搜索从而调用数十亿的 Api 时。所以一次调用数十亿个 Api 肯定会导致浏览器性能变慢。为了减少这个缺点,Debounceing 出现了。 在这种情况下,Debounce 将在两次击键之间设置一个时间间隔,假设为 2 秒。如果两次击键之间的时间超过 2 秒,则只会调用 Api。在这 2 秒内,用户至少可以输入一些字符,从而减少 Api 调用的那些字符。由于 Api 调用减少了,浏览器性能将得到提高。必须注意 Debounce 函数在每次击键时都会更新。
代码
const debounce = (func, time = 17, options = {
leading: true,
context: null
}) => {
let timer;
const _debounce = function (...args) {
if (timer) {
clearTimeout(timer)
}
if (options.leading && !timer) {
timer = setTimeout(null, time)
func.apply(options.context, args)
}else{
timer = setTimeout(() => {
func.apply(options.context, args)
timer = null
}, time)
}
};
_debounce.cancel = function () {
clearTimeout(timer)
timer = null
};
return _debounce
}10. 节流(Throttling)
节流将改变一个函数,它在一个时间内只能呗出发一次。例如,无论用户点击按钮多少次,节流后只会在 1000 毫秒内执行一次函数。

const throttle = (func, time = 17, options = {
leading: true,
trailing: false,
context: null
}) => {
let previous = new Date(0).getTime()
let timer;
const _throttle = function (...args) {
let now = new Date().getTime();
if (!options.leading) {
if (timer) return
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null
func.apply(options.context, args)
}, time)
} else if (now - previous > time) {
func.apply(options.context, args)
previous = now
} else if (options.trailing) {
clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
func.apply(options.context, args)
}, time)
}
};
_throttle.cancel = () => {
previous = 0;
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = null
};
return _throttle
};11. 图片懒加载
图片懒加载是指在网站上异步加载图片,也就是说,在上面的内容完全加载完之后,或者说有条件的,只有当他们出现在浏览器的窗口内。这就意味着,如果用户不向下滚动,放在底部的图片将不会被加载。
// getBoundingClientRect
let imgList1 = [...document.querySelectorAll(".get_bounding_rect")]
let num = imgList1.length
let lazyLoad1 = (function () {
let count = 0
return function () {
let deleteIndexList = []
imgList1.forEach((img,index) => {
let rect = img.getBoundingClientRect()
if (rect.top < window.innerHeight) {
img.src = img.dataset.src
// Add picture to delete list after loading successfully
deleteIndexList.push(index)
count++
if (count === num) {
//When all pictures are loaded, unbind scroll event
document.removeEventListener('scroll',lazyLoad1)
}
}
})
// Delete loaded pictures
imgList1 = imgList1.filter((_,index)=>!deleteIndexList.includes(index))
}
})()12. 数组随机打乱(洗牌算法)
我们经常需要去打乱一个数组。
代码
// Randomly select one of all elements after the current element to exchange with the current element
function shuffle(arr) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
let randomIndex = i + Math.floor(Math.random() * (arr.length - i));
[arr[i], arr[randomIndex]] = [arr[randomIndex], arr[i]]
}
return arr
}
// Generate a new array, randomly take an element from the original array and put it into the new array
function shuffle2(arr) {
let _arr = []
while (arr.length) {
let randomIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * (arr.length))
_arr.push(arr.splice(randomIndex, 1)[0])
}
return _arr
}案例

13. 单例模式
单例模式将限制一个对象的实例只能有一个。这个对象被称为单例。